Oahu
AIRPORTS & AIRFIELDS

John Rodgers Airport was the first airport in the Territory of Hawaii. It was dedicated on March 27, 1927. The airport was named after pioneer aviator John Rodgers who made the first trans-Pacific flight on August 31, 1925.

Honolulu International Airport
John Rodgers Airport was renamed Honolulu Airport on May 2, 1947 after it was returned to the Territory by the military after World War II. The airport was renamed Honolulu International Airport on April 27, 1951.
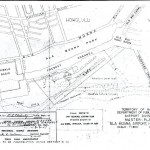
In 1944 the Territorial Department of Public Works proposed that an airport for private flying be created by a combined coral dredging and fill project on the reef between downtown Honolulu and the Waikiki section of the city.

The Ala Wai Heliport was a State-operated heliport facility located makai of the Hilton Hawaiian Village Lagoon and adjacent to the Ala Wai Yacht Harbor.

Barber’s Point Naval Air Station was commissioned on April 15, 1942. The base was decommissioned in 1998 and turned over to the State of Hawaii for use as Kalaeloa Airport, an alternate landing site for Honolulu International Airport and for general aviation purposes.

The Waimanalo Military Reservation was established in 1917. The installation was renamed Bellows Field in 1933 to honor 2nd Lt. Franklin B. Bellows.

Dillingham (Kawaihapai) Airfield
Dillingham (Kawaihapai) Airfield was originally known as Mokuleia Airfield and was established by the Army in 1922 as Camp Kawaihapai. Today it is used by the state for glider and sky diving activities.

Haleiwa Field was located on the northwest coast of Oahu, 30 miles from Honolulu. Originally (prewar) it was a center for private flying. The Army improved the field during the early part of World War II and in 1944 the Navy took the field over for carrier-landing training.

In 1934, the Army Air Corps saw the need for another airfield in Hawaii and assigned the Quartermaster Corps the job of constructing a modern airdrome from tangled brush and sugar cane fields adjacent to Pearl Harbor on the island of Oahu.

Formerly Barbers Point NAS, Kalaeloa Airport was deeded to the State of Hawaii on July 1, 1999 as a general aviation reliever airport. It also supports the U.S. Coast Guard, Hawaii National Guard and the Hawaii Community College Flight Program.

The Navy decided to acquire all of Mokapu Peninsula to expand Naval Air Station Kaneohe, a sea plane base it had begun building in September 1939 and would commission on 15 February 1941.

Kipapa Field was situated on the central plateau of Oahu 15 miles from downtown Honolulu on the road which leads to Haleiwa Airport.

On February 6, 1922, a detachment of 20 enlisted men from Luke Field, proceeded to Schofield Barracks, under Lt. William Agee, to clear the flying field and construct housing for the divisional air service.
SEAPLANE ANCHORAGES
| Honolulu | Small harbor usually congested with shipping. Planes may easily docked but good anchorage is hard to obtain. Tide flats may be used to beach planes, in sinking conditions. Prevailing winds are offshore, making take-off difficult, as it necessary to run down channel, cross wind. Very bumpy Air |
| Kailua Bay | An open bight affording emergency anchorage with no shelter from trades. Shoal water extend 7/8 miles off shore of the bay. It has telephone and small boats. The beach swells heavily and sandy. |
| Koko Head | It is an emergency anchorage in Maunalua Bay an open bight on the westerly side of Koko Head. Shoal water extends 3/4 miles from the head of the bay; there id an opening in the reef where small boats may pass to the sandy beach. It has telephones and small boats. |
| Waialua Bay | A small indentation at the bend near the middle of the northwest coast of Oahu. It has telephones and stores. The beach has heavy swells and the anchorage in creek mouth available for few planes. |
| Kaneohe Bay | Kaneohe Bay is full of reefs and shoals. In heavy trades the sea breaks across both entrances. Several villages are scatters along the shore of the bay. The village of Kaneohe is located at the southeastern end of the bay. |
| Pearl Harbor – Fleet Air Base | Naval station and Ford Island. Honolulu 6.5 miles southeast. Suitable for any size ship. United States naval base. Excellent seaplane base. |
AIR TRAFFIC STATISTICS
Honolulu International Airport Air Traffic Statistics
Dillingham Airfield Air Traffic Statistics


